Our last EMERALD fragment, “The Role of OpenNebula for the Multicloud Security-Certification Challenges of EMERALD,” explained why continuous evidence and security certification are central to the project’s mission (EMERALD).
This follow-up looks at how the same platform turns multi-cloud theory into day-to-day reality—and why that matters even more now that the EU Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) has been in force since 17 January 2025.
Why a Multi‑Cloud Setup?
Running an application on more than one cloud brings three clear advantages:
- Fewer outages – if one provider has a problem, traffic simply moves to the others.
- Smarter cost‑and‑latency choices – each service can live where price, performance, or data‑location law is best for that workload.
- True vendor freedom – organisations avoid lock‑in, which recent surveys now list as a top driver for multi‑cloud adoption.
OpenNebula makes these benefits practical with two built‑in tools:
- OneForm (coming officially in OpenNebula 7.0 and already available in the public beta) turns a short template into ready‑to‑use clusters on any public or private cloud.
- OneFlow then deploys and keeps the applications running across all clusters, no hand‑written scripts required.
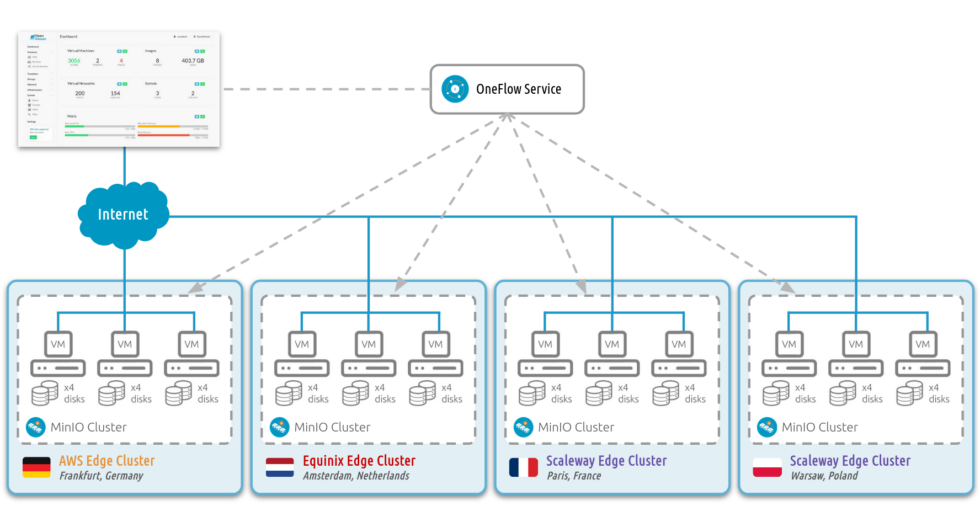
Because everything is described once and reused everywhere, teams do not have to rebuild the same setup provider by provider.
The Pilot 4: Several Clouds, One Control Plane
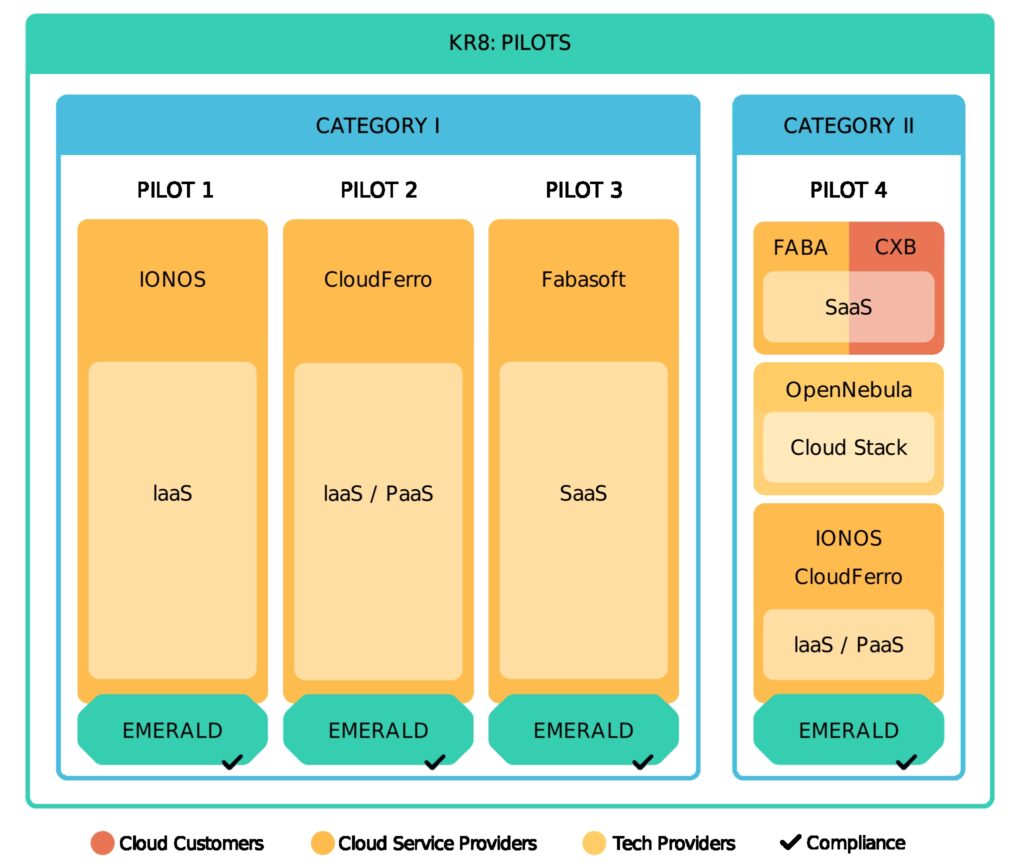
Figure 2 shows how EMERALD’s pilots map to different provider categories; Pilot 4 is the focus here. It uses four independent clouds while keeping a single control plane: OpenNebula sits in the middle as an unified Evidence-Collection Gateway. It gathers security metrics, like BSI C5 and CIS, and stores them in the EMERALD Evidence Store. Resources are deployed across three different clouds, all managed centrally from a unified dashboard:
| Cloud | Main resource |
|---|---|
| CloudFerro | VMs & storage |
| IONOS | Bare-metal servers |
| CaixaBank | On-prem VMs |
Mapping the design to DORA requirements
DORA asks financial entities to control ICT risk in five areas: governance, risk management, incident reporting, resilience testing, and third-party oversight. Our multi-cloud approach covers the hardest parts:
- No single point of failure – Workloads are split across CloudFerro, IONOS, Fabasoft, and CaixaBank. If one goes down, OneFlow shifts traffic to the others and keeps service levels within agreed recovery times.
- Proof instead of promises – Every deployment, scale-out, or fail-over event creates a signed log entry. Auditors get machine-readable evidence, not screenshots.
- Vendor-neutral tooling – All day-to-day actions use the same OpenNebula dashboard or REST API, so teams do not need to learn five different sets of commands.
These controls speak directly to DORA’s focus on concentration risk and operational continuity requirements. (The Register)
What Comes Next
The pilot shows that OpenNebula with EMERALD delivers a clear, DORA‑ready multi‑cloud blueprint without locking users to a single vendor. In the next fragment, we’ll dive into the architecture itself, covering network design, policy guards, and how the same blueprint can map to other security schemes beyond DORA.
